Webhooks
This guide will help you integrate with BaseKit’s Webhooks.
What are Webhooks
“A webhook is an HTTP request, triggered by an event in a source system and sent to a destination system, often with a payload of data. Webhooks are automated, in other words they are automatically sent out when their event is fired in the source system.” – Hookdeck
Webhooks in BaseKit can be used to connect events on the BaseKit platform, with external services.
For example, it is possible to send data to an external service, such as Zapier, each time a customer publishes their site.
How to use Webhooks
To make use of Webhooks, you must first be subscribed. This is managed by an extension to our REST API, which enables subscription management. A REST API consumer can subscribe to an event, by supplying an event to subscribe to, and a webhook URL, which our system will send a payload to.
Event Payloads
For each event on the BaseKit platform, an associated payload is sent to the connected webhook subscription.
account_holder.created
{
"eventName": "account_holder.created",
"accountHolder": {
"ref": 199,
"firstName": "Web",
"lastName": "Hook",
"email": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"username": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"created": "2023-03-06T10:15:59+00:00",
"brand": {
"ref": 1,
"name": "BaseKit Brand"
},
"packages": [
{
"ref": 1,
"name": "Demo Package",
"productType": "subscription",
"startDate": "2023-03-06T10:15:59+00:00",
"endDate": null
},
{
"ref": 2,
"name": "Add-on Package",
"productType": "add-on",
"startDate": "2023-03-06T10:15:59+00:00",
"endDate": null
}
],
"metadata": {
"key1": "value1"
}
}
}account_holder.package_change
{
"eventName": "account_holder.package_change",
"accountHolder": {
"ref": 199,
"firstName": "Web",
"lastName": "Hook",
"email": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"username": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"created": "2023-03-06T10:15:59+00:00",
"brand": {
"ref": 1,
"name": "BaseKit Brand"
},
"packages": [
{
"ref": 1,
"name": "Demo Package",
"productType": "subscription",
"startDate": "2023-03-20T14:45:02+00:00",
"endDate": null
},
{
"ref": 2,
"name": "Add-on Package",
"productType": "add-on",
"startDate": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"endDate": null
}
],
"metadata": {
"key1": "value1"
}
},
"packageChange": {
"ref": 2,
"name": "Add-on Package",
"productType": "add-on",
"startDate": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"endDate": null
}
}booking.updated
{
"eventName": "booking.updated",
"booking": {
"ref": 1036,
"customer": {
"ref": 789,
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Doe",
"email": "john.doe@website.com",
"telephone": "",
"timezone": "Europe/London",
"marketing": false,
"termsAndConditions": true
},
"status": "completed",
"payment": {
"paymentMethod": "jazzcash",
"currency": "PKR",
"netAmount": "10.00",
"totalAmount": "10.00",
"taxAmount": "0.00",
"taxRate": 0,
"taxEnabled": false,
"internalTransactionRef": "TfD6I8MmlLpOG1Iv9Fa27ejYloKx5i1q",
"externalTransactionRef": "240227563891",
"status": "completed"
},
"locationType": "other",
"location": null,
"otherJoiningInstructionsText": "",
"otherConferencingProviderUrl": "",
"service": {
"ref": 42,
"description": "A short one on one class to introduce you to the basics of yoga, matt provided.",
"duration": 30,
"active": true,
"visible": true,
"type": "appointment",
"capacity": null,
"paymentMode": "paid",
"paymentPrice": "10.00",
"advanceNoticeTime": 0,
"bufferTime": 0,
"informationDocumentDescription": "",
"bookingInformation": ""
},
"serviceSchedules": [
{
"capacity": null,
"conferenceUrl": null,
"description": null,
"start": "2024-02-28T12:00:00+00:00",
"end": "2024-02-28T12:30:00+00:00",
"bookingInformation": null
}
],
"created": "2024-02-27T17:32:37+00:00",
"updated": "2024-02-27T17:33:30+00:00"
}
}site.first_publish
{
"eventName": "site.first_publish",
"site": {
"ref": 350,
"domain": "webhooks.basekit.test",
"firstPublish": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"lastPublish": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"accountHolder": {
"ref": 346,
"firstName": "Web",
"lastName": "Hook",
"email": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"username": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"created": "2023-03-22T14:44:42+00:00",
"brand": {
"ref": 1,
"name": "BaseKit"
},
"packages": [
{
"ref": 222,
"name": "Demo Package",
"productType": "subscription",
"startDate": "2023-03-22T14:44:42+00:00",
"endDate": null
}
],
"metadata": {
"key1": "value1"
}
}
}
}site.publish
{
"eventName": "site.publish",
"site": {
"ref": 911,
"domain": "webhooks.basekit.test",
"firstPublish": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"lastPublish": "2023-03-22T14:45:02+00:00",
"accountHolder": {
"ref": 903,
"firstName": "Web",
"lastName": "Hook",
"email": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"username": "webhooks@basekit.com",
"created": "2023-03-22T14:44:42+00:00",
"brand": {
"ref": 1,
"name": "BaseKit"
},
"packages": [
{
"ref": 16,
"name": "Demo Package",
"productType": "subscription",
"startDate": "2023-03-22T14:44:42+00:00",
"endDate": null
}
],
"metadata": {
"key1": "value1"
}
}
}
}store.order_updated
{
"eventName": "store.order_updated",
"order": {
"ref": 10,
"code": "3-89696896",
"items": [
{
"title": "Home barista aeropress coffee maker",
"options": null,
"quantity": 1,
"formattedPriceTotal": "$19.99",
"formattedPriceTotalInclTax": "$23.99",
"formattedPriceUnit": "$19.99",
"sku": "3-6-6"
}
],
"subTotal": "$19.99",
"rawSubTotal": 19.99,
"rawTaxAmount": 4,
"subTotalInclTax": "$23.99",
"shippingCost": "$1.99",
"taxAmount": "$4.00",
"total": "$25.98",
"rawTotal": 25.98,
"deliveryAddress": {
"name": "John Doe",
"address1": "Address Line 1",
"address2": "Address Line 2",
"townOrCity": "Town or City",
"postcode": "BS2 0JA",
"region": null,
"countryCode": "GB",
"countryName": "United Kingdom"
},
"shippingOptionName": "UPS Next Day",
"shippingOptionCourier": "UPS",
"customerEmail": "john.doe@website.com",
"pecAddress": null,
"recipientCode": null,
"customerPhoneNumber": null,
"paymentMethod": "bank-transfer",
"paymentProcessorId": null,
"createdDate": "2024-02-27T15:48:10+00:00",
"updatedDate": "2024-02-27T15:48:25+00:00",
"shippedDate": null,
"status": "paid",
"orderComments": null,
"discountCode": "",
"discountCodeSubTotalSaving": 0,
"discountCodeShippingSaving": 0,
"discountCodeFormattedSaving": "-$0.00",
"invoiceNumber": null,
"marketingConsent": false
}
}Zapier Integration
Zapier is an automation platform that connects your apps and moves information between them based on rules you set. Zapier workflows are called Zaps and enable this connection between applications. A Zapier workflow can be initiated by a Webhook, using a trigger called “Catch Raw Hook in Webhooks by Zapier”.
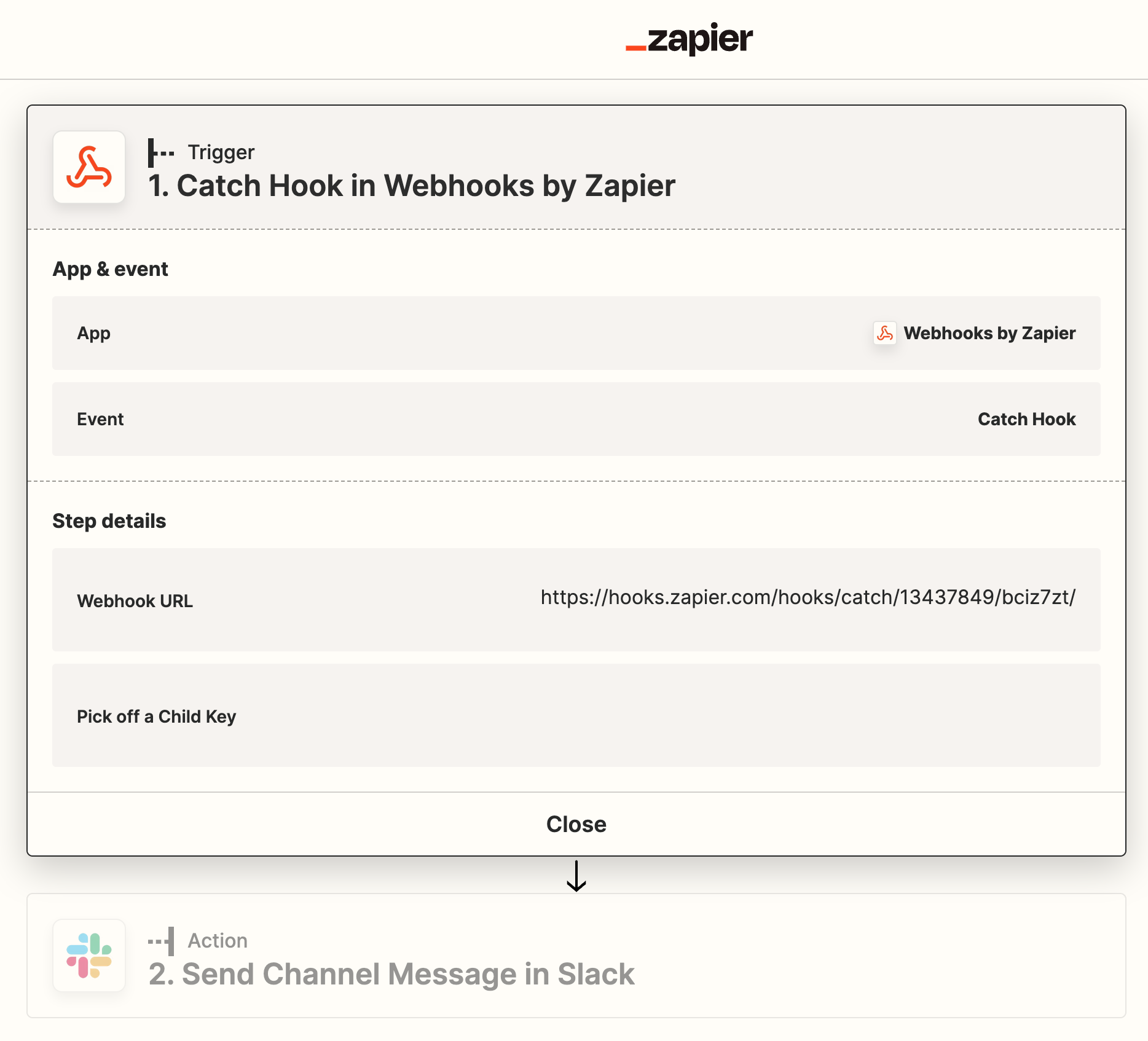
A basic Zap will look much like this

When you create an integration with BaseKit’s webhooks, you first create your Zap, and then you will find your Webhook URL within the Zapier UI as below. This URL is the URL which you create a subscription with using the Create Subscription Endpoint.
HMAC Authentication
Webhooks should always be delivered over HTTPS for security. Webhook endpoints however, by their very nature, are often open to any source system that knows their URL. A common defense to guarantee data integrity, and security from remote exploitation, is to implement HMAC Authentication. BaseKit sends a HMAC signature with all outgoing Webhooks using the X-Delivery-Hmac-SHA256 header, which a consumer can optionally validate.
To make use of HMAC Authentication you will need to request for a HMAC Secret to be generated within your environment. This secret will be used to sign the webhook when it is delivered by BaseKit, and to validate the request at the destination.
It is then possible with Zapier, for example, to validate the Webhook using an advanced workflow as below. This workflow uses Zapier Secret Storage to securely store the HMAC Secret generated above.
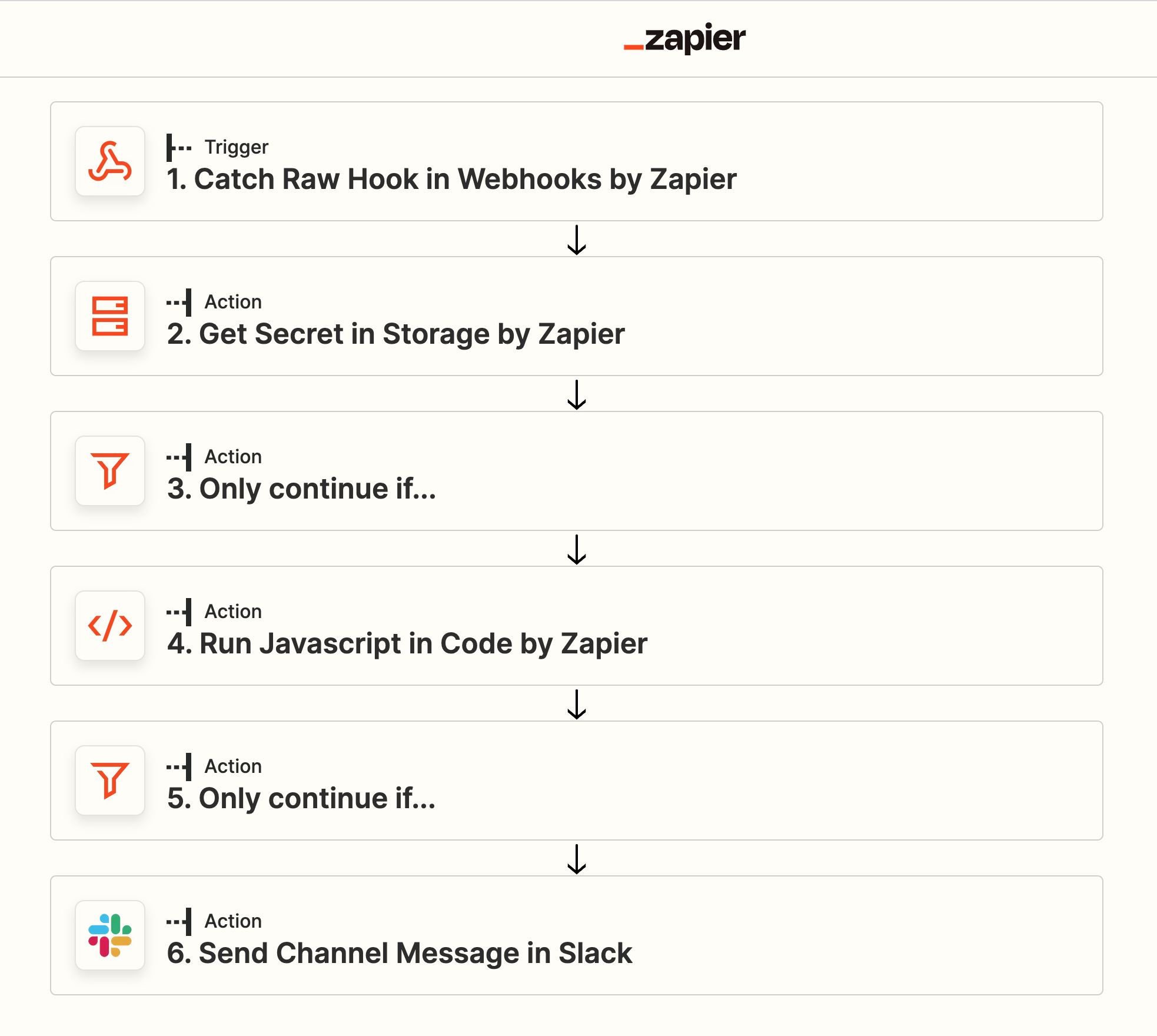
Using the “Run JavaScript in Code” trigger and the example code below, you can validate the request has originated at BaseKit.
let crypto = require('crypto');
let secret = inputData.secret;
let webhookBody = inputData.body;
let hmacSignature = inputData.hmacSignature;
let signature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secret).update(webhookBody).digest("base64");
const validSignature = (signature === hmacSignature);
output = [{isHmacValid: validSignature}];Need help?
Our teams are always on hand to assist you. For commercial enquires contact partners@basekit.com, and for technical questions integrations@basekit.com.